NOISE AND ITS IMPACT ON THE HUMAN BODY.
- 10 February 2021 22:42:27
- Reviews: 0
- Views: 2834
-

Noise is any kind of noise that is undesirable or harmful to human health and life. Noise, depending on its type, can be divided into continuous and impulse. Continuous noise is noise with small changes in intensity and frequency spectrum over time, such as noise. Impulse noise, as the name suggests, is the noise from some external impulse such as gunshots. The harmfulness of noise depends on several factors: duration of exposure to noise, intensity, frequency spectrum and how it changes over time.
The measure of noise is noise, the unit of measurement of which is noise. Just as you can measure the loudness of a sound, you can measure the noise level.
Noise can be divided according to its place of origin, noise source, etc. So, we can distinguish: industrial, road, communication, residential, residential noise, etc. Depending on the frequency, it can be low-frequency or high-frequency noise.
The negative impact of noise on a person is manifested by a feeling of discomfort, a violation of productivity and work efficiency. High-intensity noise has a destructive effect on the hearing organ, destroys the nervous system and internal organs of a person, leads to physical and mental fatigue, makes a person feel heavy, and headache and irritation may occur. Noise can disturb sleep. Please note that noise above 80 dB can cause temporary or permanent hearing loss.
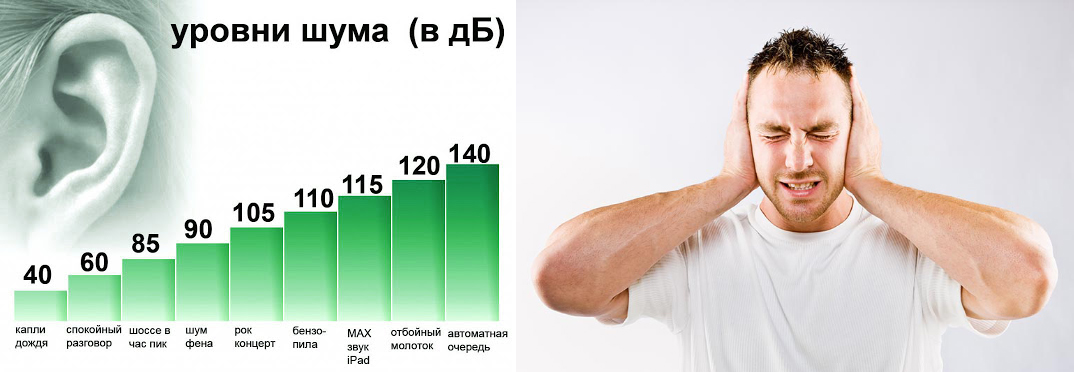
Noise levels:
35 dB or less - no harm to humans was found, but may cause irritation in sensitive people,
From 35 to 70 dB - continuous noise of this value can negatively affect the human nervous system, cause general fatigue and difficulty falling asleep, speech intelligibility decreases,
From 70 to 85 dB - for a long time causes a decrease in performance, hearing impairment, negatively affects the nervous system
From 85 to 130 - such noise impairs hearing, causes cardiovascular disorders, disturbs the sense of balance, significantly impairs speech intelligibility even at a short distance,
130-150 dB - stimulates the internal organs of a person to vibrate, causes irreversible diseases, including significant hearing loss and damage
150 or more - such noise can irreversibly disrupt the functioning of the human body, cause nausea, loss of balance, people working in such conditions often suffer from incurable diseases, and also show symptoms of mental illness.
Noise, like garbage or sewage, is considered a pollution factor, and more than half of Poland's inhabitants live in regions that are threatened by excessive noise. Residents of large cities and industrial centers, as well as people living in close proximity to major communication routes, airport stations, etc., are most susceptible to noise and its negative effects. Noise can be controlled in a number of ways, including by limiting it, eliminating it, changing manufacturing processes to quieter ones, acoustically adapting homes, schools and workplaces, and using collective or personal hearing protection.
From Ecosound's point of view, we fight noise by limiting its spread, by designing and building acoustic screens and barriers, or by increasing the insulation of acoustic partitions. In order to combat noise, we often combine muting and muting. Firstly, we try to reduce the noise at the point of origin through appropriate acoustic adaptation (damping), elimination of reflections and resonances and increasing the acoustic absorption of the room (for example, with the help of special technical sound-absorbing foams). Then, for example, by increasing the wall insulation (sound insulation) or by adding additional insulating wall cladding, we reduce the noise coming from outside. Each adaptation must be preceded by a corresponding acoustic measurement.


